No products in the cart.
Since 1990, there has been a 41% increase in Greenhouse Gas Emissions world wide.
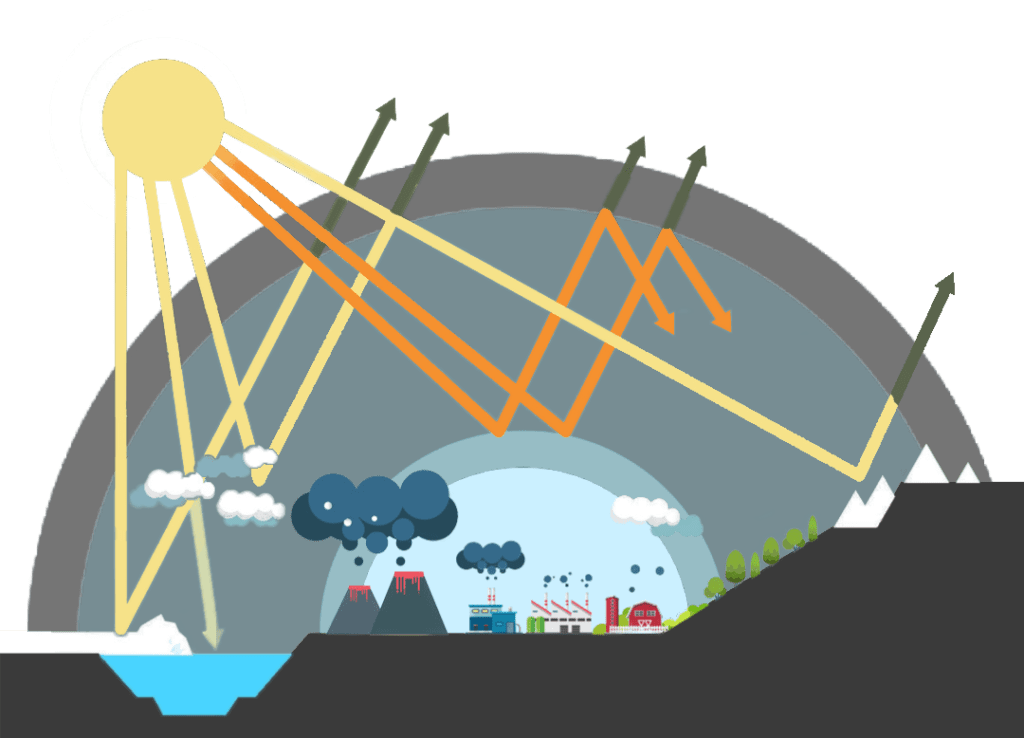
Any gas that is present in the earth’s atmosphere which can trap the heat brought in by the sunlight can is known as a Greenhouse Gas. Technically, a greenhouse gas can be defined as any gas that has the ability to absorb and emit radiant energy within the thermal infrared range.
By absorbing and emitting thermal radiation, greenhouse gases result in the greenhouse effect. This phenomenon is crucial for all life on this planet as it keeps the planet warm. It is believed that the earth would 33° C colder without the greenhouse gases making several places uninhabitable.
Types of Greenhouse Gases
There are many greenhouse gases present in the atmosphere. Some of these greenhouse gases occur naturally while the others have been introduced into the atmosphere due to human activities. Human activities have also accelerated in the emissions of naturally occurring greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
Some of the greenhouse gases are listed below:
| Greenhouse Gas | Chemical Formula |
|---|---|
| Carbon Dioxide | CO2 |
| Methane | CH4 |
| Nitrous Oxide | N2O |
| Chlorofluorocarbon - 12 | CCl2F2 |
| Hydrofluorocarbon-23 | CHF3 |
| Sulphur Hexafluoride | SF6 |
| Nitrogen Trifluoride | NF3 |
| Ozone | O3 |
Global Warming Potential of Greenhouse Gases
All the greenhouse gases differ from each other in three key aspects:
- Radiative Efficiency (Ability to absorb energy)
- At what wavelength does the gas absorb radiation
- Lifetime (Duration of stay in atmosphere)
In order to allow for comparisons among these greenhouse gases a standard was developed. This standard is also referred to as the Global Warming Potential.
IPCC 1996 defines the global warming potential as the cumulative radiative forcing – both direct and indirect effects -integrated over a period of time from the emission of a unit mass of gas relative to some reference gas.
Carbon dioxide (CO2) was chosen by IPCC as this reference greenhouse gas since it is a naturally occurring gas and plays an important role in the carbon cycle. The GWP of Carbon Dioxide is considered to be 1.
Global Warming Potential specifically refers to a measure of how much energy the emission of 1 ton of gas will absorb over a given period of time, relative to the emissions of 1 ton of carbon dioxide (CO2).
| Greenhouse Gas | Chemical Formula | Global Warming Potential | Atmospheric Lifetime (years) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Dioxide | CO2 | 1 | 100 |
| Methane | CH4 | 25 | 12 |
| Nitrous Oxide | N2O | 298 | 114 |
| Chlorofluorocarbon - 12 | CCl2F2 | 10,900 | 100 |
| Hydrofluorocarbon-23 | CHF3 | 14,800 | 270 |
| Sulphur Hexafluoride | SF6 | 22,800 | 3,200 |
| Nitrogen Trifluoride | NF3 | 17,200 | 740 |
Sources of Greenhouse Gases
All activities, natural and human, resulting in any type of emissions into the atmosphere can be considered as sources of greenhouse gases. In the past few decades, majority of the greenhouse gases released into the atmosphere due to human activities.
Some of the most common sources of greenhouse gases are listed as follows:
All of the above sources use fossil fuels either directly or indirectly releasing several pollutants into the atmosphere. While some of the pollutants directly act as greenhouse gases, the others react with existing elements from the atmosphere turning into greenhouse gases.
The following chart illustrates the approximate contributions made by the different sources of greenhouse gases.
There was an issue displaying the chart. Please edit the chart in the admin area for more details.Impacts of Greenhouse Gases
Greenhouse Gases, in controlled quantities, are supposed to result in the greenhouse effect which enables comfortable sustenance of life on this planet. But accelerated and increased rate at which greenhouse gases are being released into the atmosphere have several direct and indirect impacts. All these impacts are interlinked or connected.
Some of these impacts are:
- Increased Air Pollution
- Global Warming
- Climate Change
- Melting of Polar Ice Caps
These impacts have several adverse consequences on the environment and all its ecosystems. Some of these consequences are:
- Rising sea levels due to global warming
- Frequent Flooding of islands and coastal cities due to rising sea levels and climate changes
- Migration of Species as climate change and global warming directly affect their habitat
- Decrease in the quality of the agricultural produce due to global warming and climate change.
Summary
Article Name
Greenhouse Gases: All you need to Know
Description
Greenhouse gases have a direct impact on the environment. Since 1990, there has been a 41% increase in Greenhouse Gases world-wide.
Author
Team GreenSutra
Publisher Name
GreenSutra
Publisher Logo

1 comment
Comments are closed.